The first cars, not to mention their "ancestors" - carriages, were not equipped with shock absorbers. Their functions were partially performed by springs, springs and torsion bars. But with the increase in speeds, it became clear that elastic elements alone are indispensable - they not only do not prevent the car body from rocking, but also make it longer. Without shock absorbers, the oscillation amplitude increases, threatening the contact of the suspension parts with each other and with the road.
STRUCTURE OF THE SUSPENSION AND THE ROLE OF SHOCK ABSORBERS IN IT
Automotive suspension components fall into three categories:
1. Guides. Levers, rods, etc., which determine the nature of the movement of the wheels.
2. Elastic. The already mentioned springs, springs, torsion bars, as well as air bags and struts used on modern cars.
3. Shock-absorbing. These are the shock absorbers themselves, including modern elements of adaptive suspensions with variable characteristics.
Shock absorbers do not replace elastic elements, but complement them, restraining vibrations and vibrations of the body and the entire sprung mass of the car. A striking example of such an interaction is the shock absorber strut, widely used in the automotive industry (especially in MacPherson-type suspensions), where the hydraulic shock absorber is located inside the coils of the spring.
Although spring suspension is the most common today, shock absorbers work with other types of suspensions: spring, torsion bar, pneumatic. In addition to cars and trucks, other types of equipment are also equipped with shock absorbers: motorcycles, trailers, agricultural machinery and even aircraft.
SHOCK ABSORBER DESIGN
Since the 30s of the last century, the vast majority of cars are equipped with hydraulic telescopic shock absorbers. By design, they are divided into two main
groups:
two-pipe;
single-pipe,
and according to the materials used - oil-filled and with gas backwater. It should be noted that gas in shock absorbers does not replace oil at all, but air - its lower compressibility increases the resistance of the rod movement, although it makes the suspension stiffer.
The two-pipe design is the most common. Such shock absorbers consist of two cylinders placed one inside the other. Inside is all the main stuffing:
a piston rod equipped with bypass valves (throttles);
bottom valve, also with valves;
main oil tank;
chamber filled with air (or gas)
to compensate for the oil volume when the stem is lowered.
The space between the pipes, inner and outer, is used as an expansion tank for oil - the main working fluid of the hydraulic shock absorber.
Double tube shock absorbers have both pros and cons. Their positive qualities include:
small dimensions;
simple design;
low manufacturing cost;
high resistance to damage (thanks to the double case);
soft work;
low internal pressure.
Negative side:
insufficiently effective cooling (due to double walls);
oil cavitation (foaming after long operation) due to overheating;
Possibility of installation only with the rod up.
This design is mainly used where a smooth, soft suspension is needed for movement at low speeds.
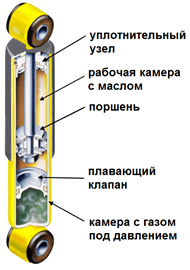
A single-tube shock absorber is devoid of most of the disadvantages of a two-tube one:
the chamber with gas is separated from the working chamber with gas by a special
floating valve to avoid foaming,
and the shock absorber itself can, if necessary, be installed under any
angle. fluctuations and vibrations.
Such shock absorbers are able to withstand severe loads without loss of performance, but are more susceptible to mechanical damage, have a longer length, and, due to the use of high-quality materials that ensure accuracy, are more expensive to manufacture. In general, shock absorbers of all types of designs are built on the same principle: when the mass of the body presses on the rod, the oil filling the shock absorber body creates resistance, slowly passing through the thin channels of the throttles (valves), slowing down